How to Understand Flu Symptoms: Learn What to Expect After Exposure in 2025
As the flu season approaches, it’s crucial to understand how to recognize the **symptoms of flu** and anticipate what to expect after exposure. Knowing the **flu incubation period** and the timelines for **flu symptoms** can help you respond effectively. This article provides a comprehensive overview of **how long does it take to get the flu**, the **flu exposure time**, and other related aspects to prepare you for the upcoming season.
Understanding Flu Symptoms
When discussing influenza, recognizing the **symptoms of flu** is paramount. Typical **flu symptoms in adults** often include fever, chills, sore throat, body aches, fatigue, and sometimes gastrointestinal issues. These signs can appear abruptly and vary in intensity from mild to severe. It’s important to note that **flu symptoms in children** might also present differently, often including more pronounced vomiting or abdominal pain. The **flu virus** spreads quickly, particularly in crowded environments, making it essential to be aware of these symptoms early on.
Flu Symptoms Timeline
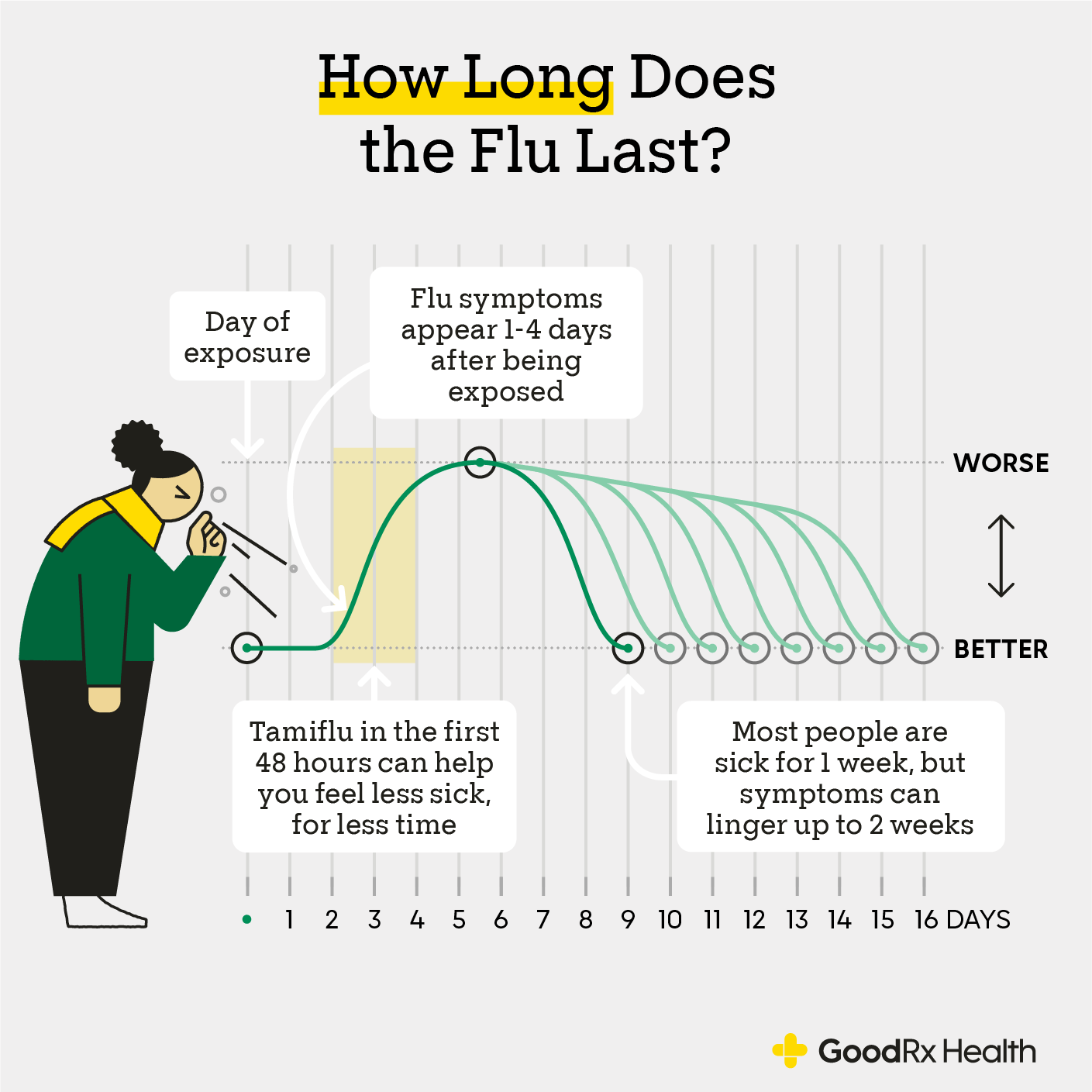
The **flu symptoms timeline** is fundamental for determining the appropriate response following exposure. After someone contracts the virus, they can expect symptoms to develop within one to four days, typically around two days post-exposure. This period is known as the **flu incubation period**. For many, recognizing early symptoms allows for timely **flu treatment options**. Should symptoms worsen or not improve within **flu illness duration**—commonly lasting one week—medical advice should be sought.
Differences Between Flu and Cold Symptoms
It can be challenging to differentiate between **flu versus cold symptoms** since they often share similar characteristics. However, while colds generally progress slowly, the flu appears suddenly and vigorously. For instance, **body aches** and **fever** are much more intense with the flu than with typical cold symptoms. Understanding these differences can assist in deciding on the necessary precautions and treatments. Parents should specifically monitor children’s symptoms closely to avoid complications.
Flu Incubation Period and Exposure Time
The **flu exposure time** and incubation period directly influence how swiftly one may develop symptoms after being infected with the **flu virus**. The average **flu incubation period** lasts approximately two days, but it can range from one to four days. Those exposed to the virus are a significant concern during this time, especially if they are in contact with vulnerable populations. Understanding this timeline allows individuals to be vigilant for symptoms and promotes better management of their health.
Flu Contagious Period
A critical aspect of flu management is understanding the **flu contagious period**. Individuals infected with the flu are generally contagious one day before symptoms appear and continue to spread the virus for about five to seven days after becoming sick. Those with weakened immune systems and young children may remain contagious for a longer time. Therefore, it is vital to minimize contact with others during this timeframe to reduce viral transmission.
Flu Transmission Methods
The **flu transmission methods** can occur through respiratory droplets, direct contact with contaminated surfaces, or from an infected individual coughing/sneezing within proximity. Understanding these methods emphasizes the importance of practicing good hygiene—such as frequent handwashing and avoiding close contact with sick individuals. Additionally, proper vaccination plays a key role in reducing the **flu transmission rate**, making it a necessary component of flu season preparations.
Flu Prevention and Treatment Options
Preventing the flu involves being aware of several **flu prevention tips**. Chief among them is vaccination. The effectiveness of the **flu vaccine effectiveness** varies yearly, but it remains one of the best defenses against seasonal flu outbreaks. Furthermore, maintaining proper hygiene, such as handwashing and using tissues to cover coughs or sneezes, can substantially decrease the chances of contracting the flu.
Flu Vaccine Importance
The **flu vaccination importance** cannot be overstated, especially for high-risk groups such as infants, elderly individuals, and those with chronic health conditions. Annual vaccinations can help mitigate severe cases and reduce hospitalizations during peak flu season. Consulting healthcare professionals to determine which vaccine is appropriate is advisable, as there are various **flu strains** in circulation each year.
Identifying Flu Complications
Recognizing potential **flu complications** is essential, particularly for vulnerable populations. Serious complications can develop, such as pneumonia or worsening of pre-existing conditions. Individuals exhibiting severe symptoms or those in high-risk groups should seek immediate medical attention, ensuring treatments are administered swiftly to mitigate the effects and improve outcomes.
Conclusion
In summary, understanding **how long does it take to get the flu** and the nuances of its symptoms aids significantly in managing your health and preventing the spread of the virus. Keeping track of the **flu contagious period**, being vigilant about symptoms, and adopting preventative measures can significantly reduce your risk of catching the flu. Emphasizing the significance of vaccines and understanding when to seek medical treatment further ensures that you prepare adequately for flu season.
FAQ
1. What is the average duration of flu symptoms?
The average duration of flu symptoms typically lasts about one week, although some individuals may experience lingering effects for a longer time, especially fatigue or cough. Proper rest and hydration are key elements in supporting recovery during this period.
2. How can I tell if I have the flu or a cold?
Flu symptoms usually come on suddenly and are more severe than cold symptoms. If you experience high fever, severe body aches, and fatigue, it is more likely to be flu rather than a cold. Monitoring symptom severity can aid in making this distinction.
3. What are the most effective flu prevention strategies?
The most effective **flu prevention strategies** include annual vaccinations, maintaining proper hygiene, regular handwashing, and avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick, particularly during flu season. Additionally, staying informed about community flu outbreaks is beneficial.
4. Can flu complications occur in healthy individuals?
While flu complications often affect high-risk groups, like the elderly, even healthy individuals can experience complications. These may vary from secondary infections to dehydration, making awareness of early symptoms and seeking treatment crucial.
5. What should I do if I think I have the flu?
If you suspect you have the flu, it’s important to stay home, rest, and maintain hydration. Over-the-counter medications can help manage symptoms. If conditions worsen or if you are in a high-risk category, seek immediate medical advice for possible antiviral treatments.
6. Are there home remedies for managing flu symptoms?
Yes, several **flu home remedies** such as herbal teas, honey, and warm broth can alleviate symptoms. Resting in a cozy environment and staying hydrated support overall recovery. However, consult with a healthcare provider for persistent or severe symptoms.
7. How do I determine if I should get a flu vaccine?
Recommendations for receiving a flu vaccine generally depend on personal health history and local flu activity. Speak with your healthcare provider to make an informed decision tailored to your specific health concerns and lifestyle, considering factors such as age and overall health.