Effective Ways to Find the Volume of a Triangular Prism
Understanding the Triangular Prism Volume Formula
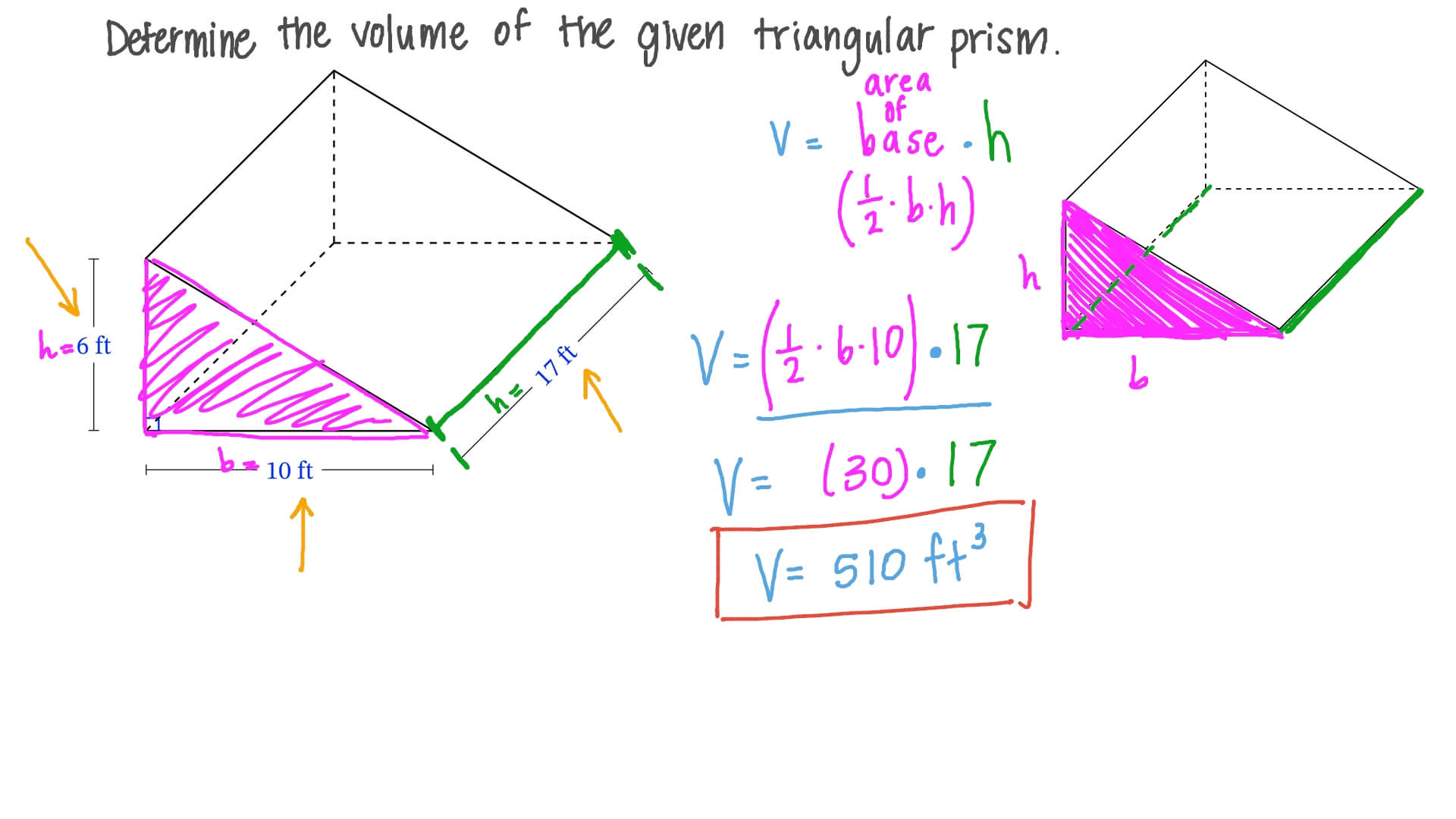
To effectively calculate the volume of a triangular prism, it’s essential to familiarize ourselves with the triangular prism formula. This formula allows us to determine how much space the prism occupies. The key components consist of the area of the triangular base and the prism’s height. The triangular prism volume formula is encapsulated in the equation: Volume = Base Area × Height. Here, the base area refers to the area of the triangular face, and knowing how to calculate this area is crucial for computing the full volume. By understanding these components, we pave the way for accurate volume calculations in geometry.
Calculating the Triangular Base Area
The first step in finding the volume of a prism involves figuring out the triangular base area. The area of a triangle can be calculated using the formula: Area = 0.5 × Base × Height of the triangle. For example, if a triangular base has a base length of 6 cm and a height of 4 cm, the area calculation will be: Area = 0.5 × 6 × 4 = 12 cm². This result indicates the size of the triangular base integral to our final volume calculation.
Height Measurement of the Triangular Prism
Once the base area is determined, the next step is to ascertain the height of the triangular prism. The height of the triangular prism represents the perpendicular distance between the two triangular bases. To visualize this, imagine a slab where the triangular bases are the top and bottom faces stacked up. Accurate height measurement is critical; otherwise, the overall volume calculation will falter. For example, if the height of the prism is measured to be 10 cm, this figure must be recorded for calculating volume.
Combining Base Area and Height for Volume Calculation
Now that we have both the base area and the height of the prism, we can insert these values into the volume formula. Continuing with our previous example, if the base area is 12 cm² and the height is 10 cm, our calculation would be: Volume = Base Area × Height = 12 cm² × 10 cm = 120 cm³. This example not only demonstrates how to calculate the volume of a triangular prism but also emphasizes the importance of each measurement. Once we comprehend this process, we can tackle various geometry problems that require volume calculations.
Applying Volume in Real-World Contexts
Understanding the volume of solids, like triangular prisms, is vital in many fields. **Volume applications** extend beyond mathematics; they feature prominently in engineering, architecture, and even culinary arts. For instance, chefs may envision the volume of a triangular cake slice to correctly layer their baking pan, while architects apply the volume of prisms in designing elements of buildings. Recognizing these real-world connections enhances the learning experience and allows students to appreciate the importance of volume calculations.
Geometric Shapes Volume in Real Life
Consider a triangular prism built with a height of 15 cm and a triangular base area of 8 cm². To find the optimal material needed for its construct, engineers calculate its volume using the volume formula mentioned above. The result becomes a metric to measure strength and the amount of raw material required. Understanding how the geometric shapes volume integrates with practical applications fosters a sense of purpose in mastering calculations related to solid volumes.
Volume Challenges in Education
In educational contexts, challenges may arise where students must calculate the volumes of differently shaped prisms, accommodating diverse parameters. For example, they may be given a rectangular prism and a triangular prism to compare their volumes. Engaging students in volume problems not only reinforces their understanding but also encourages mastery of all geometry formulas needed for accurate volume measurement.
Visualization Techniques for Better Understanding
Employing visualization techniques such as 3D modeling or using physical objects can aid tremendously in grasping the concept of volume. Students can use block models or digital resources that illustrate the expansion of volume concepts in 3D spaces. Educational math tools and visual aids can encourage engagement and help students retain knowledge regarding various triangular prism characteristics and their volumes. Whether it’s through hands-on geometry activities or simulation software, integration into lessons ensures a well-rounded comprehension.
Step-by-Step Volume Calculation Techniques
Effective volume calculations, especially for solids, often involve breaking the process into manageable steps. Here’s a straightforward approach to finding the volume of a triangular prism: first, identify the prism’s triangular base dimensions. Then, calculate the triangular area. After this, accurately measure the height of the prism. Lastly, apply the triangular prism volume formula to yield the volume. This systematic thinking is a powerful tool when solving math tutorials or working through geometry exercises.
Engaging Students with Hands-on Activities
Engaging math activities can further enhance students’ understanding of volume calculations. For instance, educators may direct students to construct their triangular prisms using paper, or they might calculate volumes using real-life objects. By finding the volume of a bottle or cardboard container shaped like a prism, learners grasp mathematical principles while enjoying a practical approach to geometry.
Classroom Techniques for Teaching Volume Concepts
Adopting new instructional methods can significantly improve the teaching of volume concepts. Introducing cross-curricular links, like the relationship between geometry and art, or connecting these ideas with other sciences (e.g., understanding drainage in earth science, agricultural practices, etc.) also establishes a broader realm of knowledge for students. Thus, educators should explore interdisciplinary teaching strategies while addressing volume theories and principles.
Key Takeaways
- Volume of a triangular prism can be calculated using the formula: Volume = Base Area × Height.
- Needing to find the area of the triangular base involves using the formula: Area = 0.5 × Base × Height.
- Real-world applications of volume underline practical instances in engineering, architecture, and everyday tasks.
- Combining hands-on learning strategies with formal teaching fosters deeper understanding.
- Visualization aids effectively support conceptual mastery of geometric shapes and volumes.
FAQ
1. What is the triangular prism definition?
A triangular prism is a type of solid geometric figure that has two identical triangular bases connected by three rectangular sides. This unique structure plays a crucial role in understanding the fundamental characteristics of prisms and their respective geometric properties.
2. How can I find the triangular base area quickly?
To find the triangular base area quickly, you can use the simple formula: Area = 0.5 × Base × Height. By knowing the base length and the height from the base to the top vertex of the triangle, you can efficiently compute the area required for the overall volume calculations.
3. What are some engaging activities to teach about volume?
Engaging activities might include using 3D models made from everyday materials, solving puzzles related to volume, or conducting experiments like filling containers with different shapes to compare volumes. Such hands-on experiences promote learning and retention while making geometry exciting.
4. How do I measure the height of a triangular prism accurately?
The height of a triangular prism is measured perpendicular to its triangular bases. Using measuring tools like a ruler or a caliper ensures you get accurate dimensions necessary for the volume calculation. It is advisable to take multiple measurements to confirm accuracy.
5. Why is understanding volume important in different fields?
Understanding volume is crucial in fields such as engineering, architecture, and various sciences. It assists professionals in material estimation, design planning, and ensuring efficient workings of products within specified dimensions, leading to more informed decision-making in their respective areas.
6. What methods can improve volume calculation efficiency?
Employing methods such as breaking down complex shapes into smaller components, utilizing calculators for complex calculations, and practicing frequent problem-solving strategies can significantly improve volume calculation efficiency. Additionally, interactive software or online resources can provide practice.
7. How can I convert volume units effectively?
To convert volume units effectively, it’s helpful to know the relationships between different units (e.g., 1 liter = 1,000 cubic centimeters). A conversion factor can aid in transitioning between units. Understanding these relationships streamlines measurements and ensures efficiency in calculations.