Essential Guide to Finding the Surface Area of a Rectangular Prism in 2025
Understanding how to calculate the surface area of a rectangular prism is fundamental in geometry, applicable across various real-world situations. This guide will take you through the essential concepts, formulas, and methods for mastering area calculations of these geometric shapes. With detailed explanations, practical examples, and engaging exercises, you will be equipped to tackle any related math problems effectively in 2025 and beyond.
Understanding Surface Area in Geometry
Surface area is a vital concept in mathematics and geometry that measures the total area that the surface of a three-dimensional object occupies. In the case of a rectangular prism, it consists of two parallel rectangular bases and four rectangular sides. To derive this measurement effectively, one must grasp the significance of dimensions shared by the prism.
Defining Surface Area
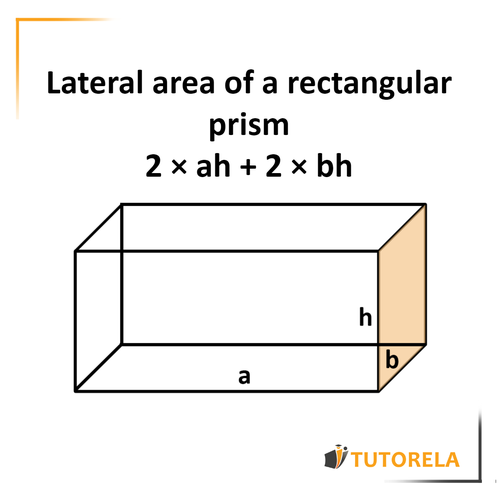
Surface area is often defined as the sum of the areas of each face of a three-dimensional shape. For a rectangular prism, the formula to calculate surface area (SA) is:
SA = 2(length × width) + 2(length × height) + 2(width × height). This highlights the three pairs of identical faces in the prism. Using dimensional analysis, we can ensure that our calculations are consistent and accurate.
Formula Application Through Examples
Let’s look at an example of a rectangular prism with dimensions of length 5 cm, width 3 cm, and height 4 cm. Applying the surface area formula, we can derive:
SA = 2(5 × 3) + 2(5 × 4) + 2(3 × 4) = 30 + 40 + 24 = 94 cm². This example illustrates a practical approach to area calculation examples in a classroom setting.
Interactive Learning Techniques
Utilizing interactive learning methods enhances student engagement in understanding the concept of surface area. Incorporating visual aids for geometry, such as 3D models or educational software, can provide students with a tactile insight into the geometric properties of prisms. This fosters an environment of hands-on learning where shape recognition grows, enabling students to visualize surface area relationships more effectively.
Practical Applications of Surface Area
Understanding the surface area of a rectangular prism is not just an academic exercise; it has significant implications in real-world applications. From packaging design to architecture, surface calculations play a crucial role. In this section, we will explore the diverse implementations and relevance of this knowledge.
In-Class Geometry Discussions
Encouraging in-class discussions around geometry-related topics aids in problem-solving skills. Students can work together to calculate the surface area of various shapes, allowing for a collaborative learning experience. Discussions may revolve around practical scenarios, such as determining how much wrapping paper is needed for gifts, reflecting real-life geometry practices.
Geometric Representations in Design
Incorporating surface area concepts in design projects showcases the practical aspects of mathematical literacy. For instance, students could create a model of a storage box and find the surface area needed for painting it. This type of project bridges theoretical calculations with practical mathematics, demonstrating the importance of understanding surface area.
Online Geometry Calculators for Hands-on Learning
Integrating online geometry calculators into lessons allows students substantial opportunities to explore surface area fundamentals. These tools are excellent for reinforcing area calculation techniques as they enable quick input and calculation of values. Furthermore, when students take charge of their learning through these resources, it fosters greater engagement and retention, leading to better academic achievement.
Geometric Analysis and Modelling
Studying geometric transformations and the attributes of rectangular prisms require a clear grasp of their properties. This knowledge enables learners to approach different geometric calculations with confidence. We will now dive into advanced concepts involving geometry.
Understanding Geometric Properties of Prisms
The geometric properties of rectangular prisms include their faces, vertices, and edges—each contributing to the formation of shapes. Recognizing these properties helps students develop valuable cognitive processes when discussing geometric representations and shape comparisons. For example, knowing the number of faces—6 in the case of a rectangular prism—can provide context for coupled area and perimeter calculations.
Exploring Relationships Between Surface Area and Volume
Another critical area of exploration involves the relationship between surface area and volume. By comparing these two aspects, learners gain a unique insight into the dimensional analysis of geometric shapes. For instance, knowing how surface area affects the volume of a box when dimensions change reinforces the practical applications of geometric principles.
Assessing Student Understanding Through Surface Area Models
Utilizing surface area models in assessments fosters an effective learning environment. Teachers can evaluate student understanding by assigning projects involving the calculation of the surface area of various shapes. This surface area theory application validates their learning outcomes in geometry. It enriches their overall understanding and development of mathematical skills required for advanced concepts.
Key Takeaways
- Surface area is crucial for both academic and practical applications, as it measures the total area of a 3D object.
- The formula for surface area of a rectangular prism is essential for conducting accurate calculations.
- Utilizing interactive tools and visual aids engages learners and enhances their understanding of geometric concepts.
- Real-life applications of surface area reinforce its significance within mathematics and everyday scenarios.
- Assessing understanding through practical examples helps strengthen students’ skills in geometry.
FAQ
1. What is the formula for the surface area of a rectangular prism?
The surface area of a rectangular prism is calculated using the formula: SA = 2(length × width) + 2(length × height) + 2(width × height). This formula accounts for the different face areas of the prism and sums them together to get the total surface area.
2. How can I apply surface area in real-life situations?
Surface area can be used in many practical scenarios like calculating the amount of paint needed for a wall, packaging dimensions for products, or even the amount of material needed to build a structure. Understanding how to derive surface area is essential for these real-world applications.
3. What are some effective tools for learning surface area?
Interactive learning tools such as dynamic geometry software and online calculators greatly enhance learning outcomes in geometry. These resources allow students to visualize geometric shapes, engage in practical exercises, and apply their knowledge creatively.
4. How does understanding surface area benefit a student’s math skills?
Mastering surface area calculations develops a student’s mathematical literacy and problem-solving skills. It encourages critical thinking and an analytical mindset, essential for success in various fields that involve geometry, such as architecture and engineering.
5. Can visual aids really help in understanding surface area?
Absolutely! Visual aids, such as diagrams and 3D models, clarify complex geometric concepts and are invaluable for students learning about surface area. They enhance comprehension by allowing students to visualize the shapes they are working with, ultimately leading to a deeper understanding of geometry.